Creating crystals
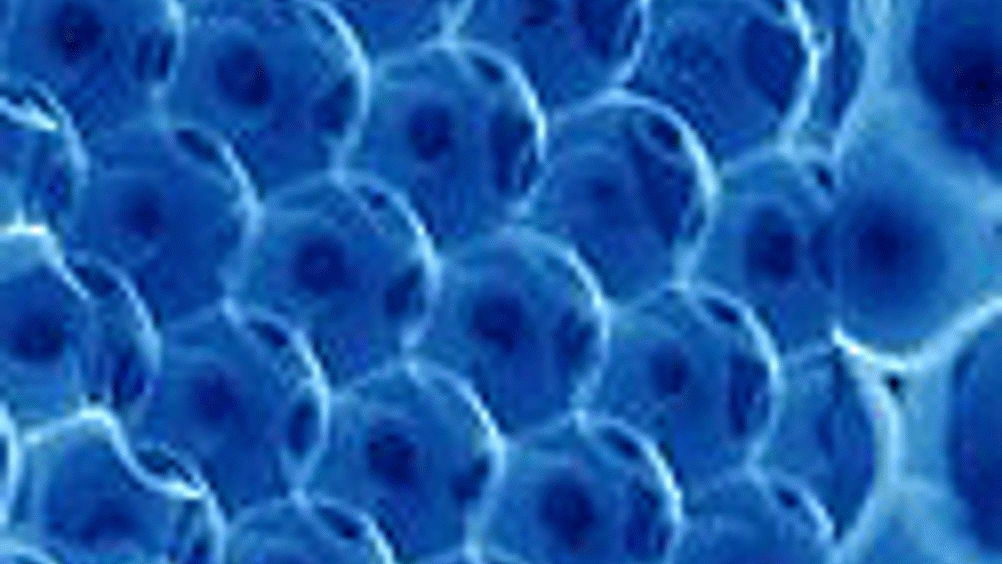
Materials scientists at
In a recent issue of the American Chemical Society journal Langmuir, Rutgers scientists and collaborators from Ceramare Corporation and the
The resulting orderly array of particles mimics the performance of traditionally fabricated crystalline wafers, without the time and expense of growing crystals in a molten mixture or solution, then slicing them into thin layers.
"The materials we've created in our lab bridge the gap between single-crystal materials, with their precisely ordered atomic structures, and ceramics, which have randomly oriented structures," said Richard Riman, professor of ceramic and materials engineering. "These so-called 'single-crystal-like' materials possess properties approaching those of true single crystal materials, but since we make them with techniques drawn from ceramic fabrication, there is potential to synthesise them economically and in large size and quantity."
Register now to continue reading
Thanks for visiting The Engineer. You’ve now reached your monthly limit of news stories. Register for free to unlock unlimited access to all of our news coverage, as well as premium content including opinion, in-depth features and special reports.
Benefits of registering
-
In-depth insights and coverage of key emerging trends
-
Unrestricted access to special reports throughout the year
-
Daily technology news delivered straight to your inbox










Water Sector Talent Exodus Could Cripple The Sector
Maybe if things are essential for the running of a country and we want to pay a fair price we should be running these utilities on a not for profit...