Page-Roberts unveils longer-range EV design
Automotive start-up Page-Roberts has patented a design concept for an electric vehicle reportedly capable of travelling up to 30 per cent further than current EVs.
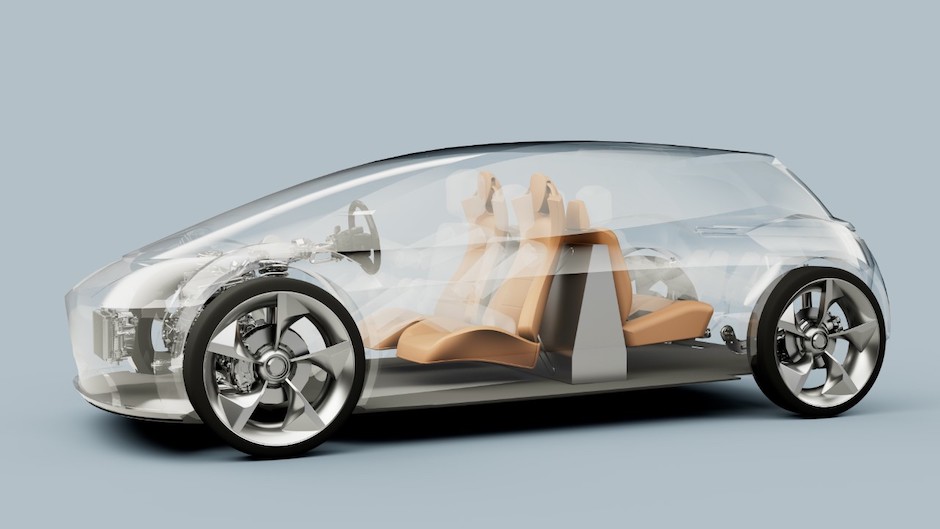
The new design positions the battery between the front row seats and a second row of rear-facing seats, disrupting the traditional ‘skateboard’ arrangement with EV batteries placed under the floor. Drawbacks of this can include added height, increased weight, structural complexities, and an extended wheelbase.
According to Page-Roberts, its arrangement will result in a lower, lighter and more aerodynamic vehicle with a standard wheelbase. Range could be extended or a smaller battery could be used to achieve a similar range to current EVs on the market, the start-up said, with potential for manufacturing costs to be cut by ‘up to 36 per cent’.
WAE and Italdesign partner for EV solution
Surrey team to improve torque vectoring
“Rear-facing seats are widely used in taxis and camper vans and may even become the norm for automated vehicles,” said CEO Freddy Page-Roberts. “Aside from the obvious benefits of increased design flexibility, they provide excellent outward visibility — a key factor for boosting occupant comfort. Their position ahead of the rear wheels also offers enhanced passenger protection — reduced whiplash, for example, in the case of frontal impact.”
Register now to continue reading
Thanks for visiting The Engineer. You’ve now reached your monthly limit of news stories. Register for free to unlock unlimited access to all of our news coverage, as well as premium content including opinion, in-depth features and special reports.
Benefits of registering
-
In-depth insights and coverage of key emerging trends
-
Unrestricted access to special reports throughout the year
-
Daily technology news delivered straight to your inbox










UK Enters ‘Golden Age of Nuclear’
The delay (nearly 8 years) in getting approval for the Rolls-Royce SMR is most worrying. Signifies a torpid and expensive system that is quite onerous...