Tumble drying culpable for release of airborne microfibres
Tumble drying laundry releases nearly the same amount of microfibres into the air as those released down the drain when the same load is machine washed.
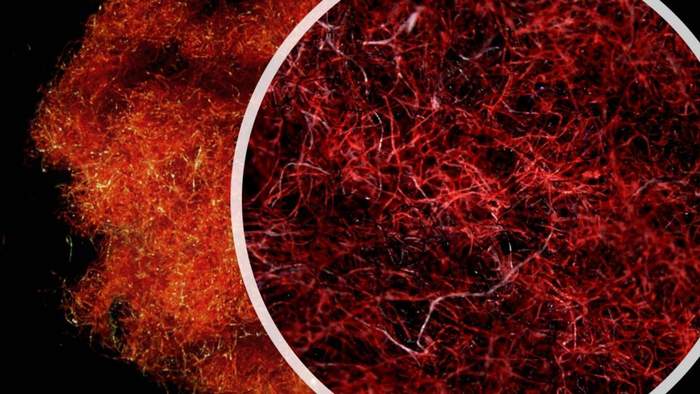
This is conclusion of research carried out by a team from Northumbria University and partners at Procter & Gamble whose findings are published in PLOS ONE.
The team found that the use of fabric conditioners and dryer sheets, especially in combination, could significantly reduce microfibre release from tumble dryers.
They also found that lint filters with smaller pores would trap larger masses, resulting in far fewer microfibres being released into the air, and that lint filters were better at capturing polyester fibres than cotton fibres, which indicates that most microfibers released into the air by dryers are likely to be cotton.
MORE FROM ENERGY & ENVIRONMENT
While extensive research has been carried out into the quantities of microfibres released down the drain by washing machines, far less is understood about the release from tumble dryers.
Register now to continue reading
Thanks for visiting The Engineer. You’ve now reached your monthly limit of news stories. Register for free to unlock unlimited access to all of our news coverage, as well as premium content including opinion, in-depth features and special reports.
Benefits of registering
-
In-depth insights and coverage of key emerging trends
-
Unrestricted access to special reports throughout the year
-
Daily technology news delivered straight to your inbox










Renewables Surge But Emissions Continue To Creep Up
"While power systems in many countries are on the cusp of – and in some cases have reached – decarbonisation" Only countries with good...