Video of the week: Graphene moves speakers out of the box
Scientists have created a new type of flat speaker that uses a graphene aerogel to create thermoacoustic sound, rather than sound through vibrations.
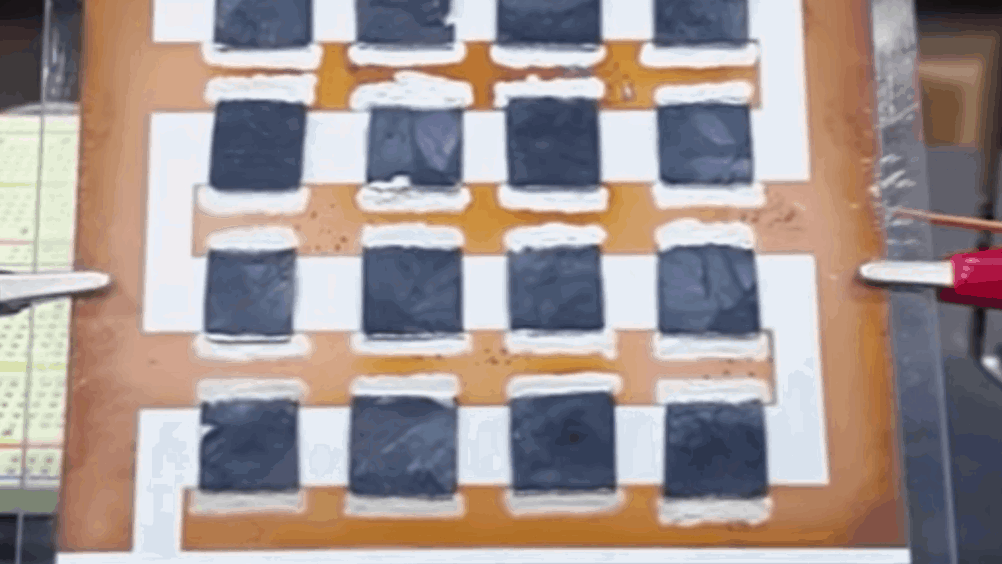
The speaker works by rapidly heating and cooling air, and because it doesn’t require a box to create vibrations, it can exist as a flat or even curved surface. Researchers from the Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST) developed a two-step (freeze-drying and reduction/doping) technique for producing the graphene aerogel. An array of these aerogels was then aligned in a 4x4 configuration to form a 40W speaker. The work, which was supported by the Samsung Research Funding Center for Future Technology and the National Research Foundation of Korea, is described in the journal ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces.
Register now to continue reading
Thanks for visiting The Engineer. You’ve now reached your monthly limit of news stories. Register for free to unlock unlimited access to all of our news coverage, as well as premium content including opinion, in-depth features and special reports.
Benefits of registering
-
In-depth insights and coverage of key emerging trends
-
Unrestricted access to special reports throughout the year
-
Daily technology news delivered straight to your inbox










Pipebots Transforming Water Pipe Leak Detection and Repair
Fantastic application.