Scaffold process could lead to new-generation MEMS devices
A new generation of microscopic devices with properties such as resistance to corrosion and heat might be possible thanks to research from physicists at Brigham Young University in Utah.
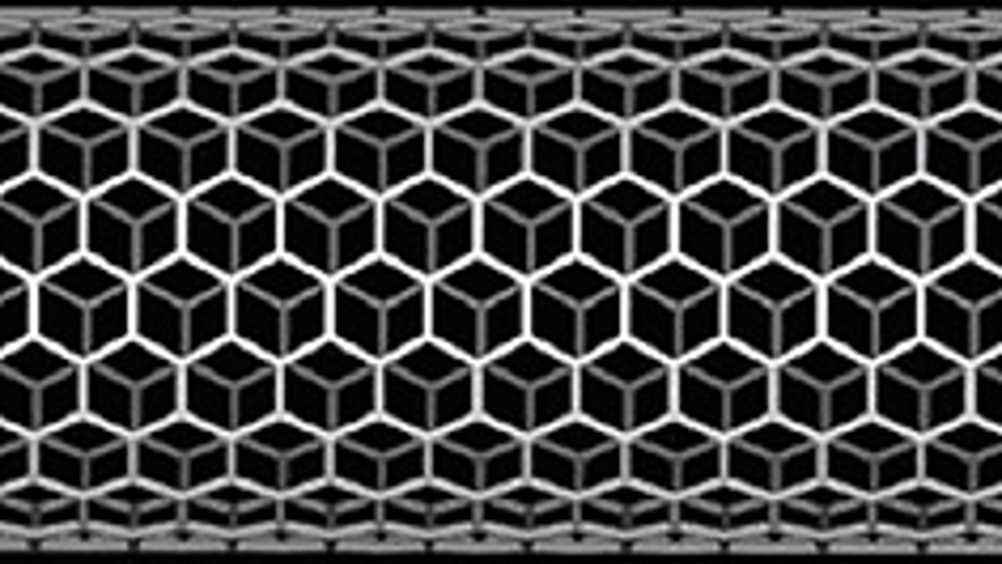
Using carbon nanotubes as part of a reinforcing structure, the team claims to have opened the possibility of using previously unused materials to build microelectromechanical system (MEMS) devices.
Generally, MEMS devices such as accelerometers and loadcells are made from silicon or silicon-based materials and are built using techniques similar to those used to make electronic components. Other materials that might be useful, including ceramics, metals and other semiconductors, generally aren’t used because the techniques to manipulate them and build them into complex shapes have not been available, according to the Brigham Young team.
The team has devised a method called carbon nanotube templated microfabrication (CNT-M), which uses arrays of vertically aligned nanotubes — known as ‘forests’ — as a scaffolding to support the deposition of these non-typical MEMS materials. Using this scaffolding, the physicists claim to have built tall, narrow, three-dimensional microstructures from tungsten, molybdenum and nickel, which have properties such as high electrical and thermal conductivity, a high melting point, corrosion resistance, low thermal expansion and hardness.
Register now to continue reading
Thanks for visiting The Engineer. You’ve now reached your monthly limit of news stories. Register for free to unlock unlimited access to all of our news coverage, as well as premium content including opinion, in-depth features and special reports.
Benefits of registering
-
In-depth insights and coverage of key emerging trends
-
Unrestricted access to special reports throughout the year
-
Daily technology news delivered straight to your inbox










CCC Report Finds UK Climate Targets Still Within Reach
In 1990 67% of the UK´s electricity came from coal-fired power stations and even without renewables the transition to gas was a major contributor to...